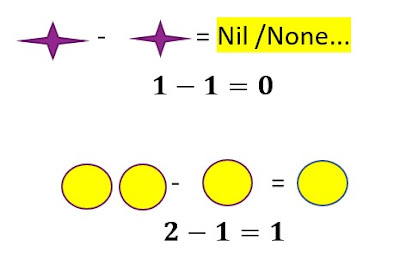
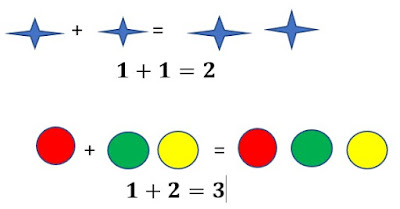
The beauty of Mathematics depends on basic four arithmetic Operations along with some functional operation:-
- Addition ( + )
- Subtraction ( - )
- Multiplication ( x )
- Division (÷) So, we shall discuss the fourth operation Division.
DIVISION
Generally, Division symbol (
÷)having a horizontal line a dot below and another at above , OR " / " ( Read as a fraction Bar or Solidus) is often used to indicate mathematical division from ancient times. The result is expressed with equals " = " symbols.
it is a basic arithmetic operation that represents the operation of repeated subtraction of objects from a given collection. The result of the division is also called a Repeated Subtraction.
The division is considered as Reciprocal of multiplication and can be learned as follows:-
4
÷ 1 = 4 means how many times one can be subtracted from 4 to get Remainder 0. 4
-1 ( Once subtracted )
------------
3
-1 ( Twice subtracted )
-------------
2
-1 ( Thrice subtracted )
------------
1
-1 ( Fourth times subtracted )
------------
0 ( Remainder)
-------------------
Since 1 is repeatedly subtracted FOUR times so answer of 4
÷ 1 is 4.The simplest way of viewing division is in terms of QUOTIENT: from the quotient perspective, 15 / 5 means the number of 5s that must be added to get 15. In terms of partition, 15 / 5 means the size of each of 5 parts into which a set of size 15 is divided. For example, 15 apples divide into five groups of THREE apples, meaning that fifteen divided by five is equal to Three. This is denoted as 15/ 5 = 3, or 155 = 3.
The number / Polynomial which divided is known as Dividend and the obtained result is called Quotient, The number from divided is called as Divisor. In the example, 15 is the dividend, 5 is the divisor, and 3 is the quotient, and Remainder is zero.
- 15-5 ( Once subtracted )------------10-5 ( Twice subtracted )--------------5 ( Thrice subtracted )------------0 ( Remainder) Therefore 15 /5 = 3.
- BY DIVIDING NUMBERS ZERO ( 0)
1
÷ 0 = ???? means how many times ZERO can be subtracted from 4 to get Remainder 0.
1
-0 ( Once subtracted )
------------
1 ( Remainder)
-------------
1 ( Remainder)
-0 ( Thrice subtracted )
------------
1 ( Remainder)
-0 ( Fourth times subtracted )
------------
1 ( Remainder)
-0
---------
1 ( Remainder)
IN ALL CASES REMAINDER IS SAME TO THE DIVIDEND 1 SO IF WE USE THIS PROCESS UNCOUNTED NUMBER OF TIMES THEN Remainder IS ALWAYS 1 ( DIVIDEND ), SO DIVISION OF ZERO IS NOT POSSIBLE OR RESTRICTED.
1
÷ 0 = ???? ANSWER - NOT POSSIBLE.
By Division of zero to any positive numbers, is not possible.
- BY DIVISION OF ONE (1)
1
÷ 1 = 1
2
÷1 = 2 - (1 + 1 ) = 2 ( Twice subtracted)
3
÷1 = 3 - (1 + 1 + 1 ) = 3 ( Thrice subtracted)
4
÷ 1= 4 - (1 + 1 + 1 + 1 ) = 4
6
9
10
÷ 1= 6 - ( 1 + 1 + 1+ 1 + 1 + 1 ) = 6
7
8 ÷1= 7 - (1 + 1 + 1+ 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 )= 7÷1 = 8 - (1 + 1 + 1+ 1 + 1 + 1 +1 + 1 ) = 89
÷ 1 = 9 - (1 + 1 + 1+ 1 + 1 + 1 +1 + 1 + 1) = 910
÷ 1= 10 - (1 + 1 + 1+ 1 + 1 + 1 +1 + 1 + 1 +1 ) = 10 ( Ten times subtracted)
...
8
÷ 2 = 4
12
÷ 2 = 6 18 ÷ 3 = 6 100 ÷ 10 = 10
21
÷ 7 = 3
similarly, more results can be verified.
--------------------