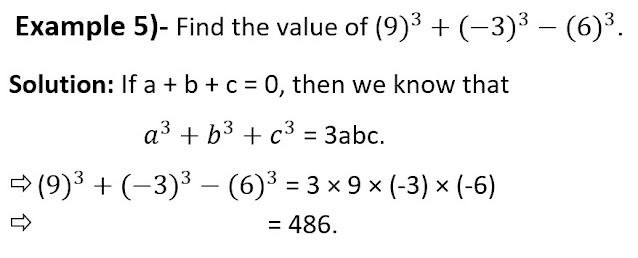What is a formula? We can say 'Any conventional or fixed methods based on experiences for doing something' or literally 'a set form of words, as for stating or declaring something definitely or authoritatively, for indicating procedure to be followed, or for prescribed use on some ceremonial occasion' is the general meaning of the formula. Mathematically we can express formula as 'A principle or rule which is frequently expressed in the language of Mathematically symbols'.
Similar to other physical science, computational, and engineering subjects mathematics is also has varied and the vast list of formulas. Classification of formulas can be done according to standard (Class) or Branches of Mathematics. In my opinion, it is beneficial to classify on the basis of Branches of Mathematics is more useful so we can classify such as
- Mathematics Formula Algebra
- Mathematics Formula Geometry
- Mathematics Formula Commercial mathematics
- Mathematics Formula Mensuration
- Mathematics Formula Trigonometry
- Mathematics Formula Coordinate Geometry
- Mathematics Formula Statistics & Probability
- Mathematics Formula Calculus
- Mathematics Formula Miscellaneous
Mathematics Formula Algebra
In algebra, we have various topics having formulas and identities, Some are listed below:-
- Algebraic Identity
- Exponents and Powers
- Least Common Multiple (LCM) & Highest Common Factor(HCF)
Now we shall write about algebraic identities.
Algebraic identities are algebraic equations that are true for all the variables involving in it. Algebraic identities are also an integral part of Formula in Algebra. These identities contain various constants and variables on both sides of the equation. When we factorize a polynomial, we often use these algebraic identities. On the basis of terms of identities, it can be divided into two parts.
- Binomial Algebraic Identity
- Trinomial(Polynomial) Algebraic Identity
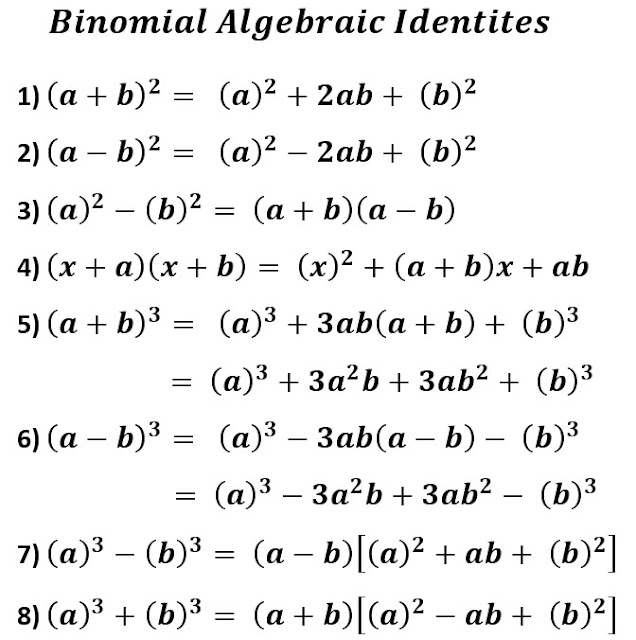
Binomial Algebraic Identity
We know that the algebraic expression having two terms is known as Binomial. The few basic important algebraic identities frequently used in algebra as well as other branches of mathematics are such as( Instead of a and b we can use any alphabets of many languages).
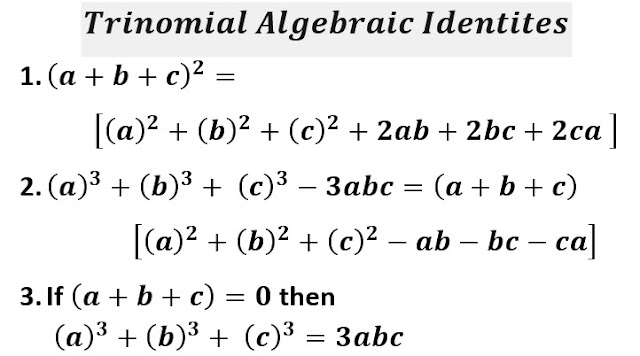
Trinomial(Polynomial) Algebraic Identity
The algebraic expression having three terms is known as Trinomial. The few basic important algebraic identities frequently used in algebra as well as other branches of mathematics are such as( Instead of a and b we can use any alphabets of many languages).
The First Four Binomial Algebraic Identities are in the syllabus of Middle Standard (Class 6 to 8) While all remaining along with Trinomial(Polynomial) Algebraic Identityare used in secondary Standards in mathematics.
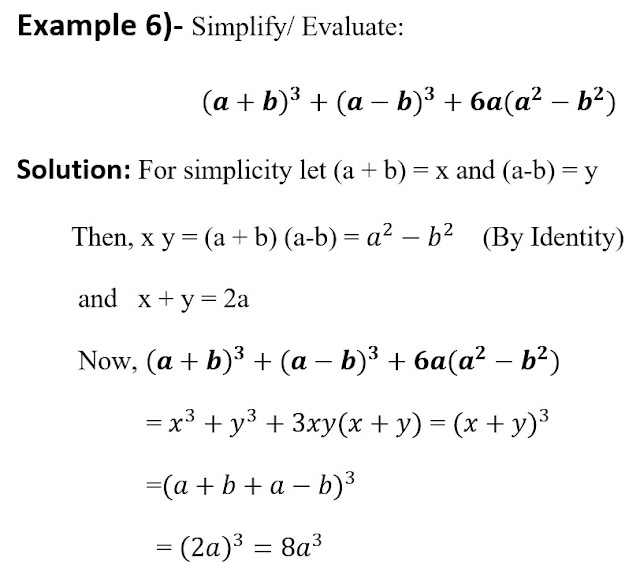
We can use the above identities to solve problems, Few illustrations are such as
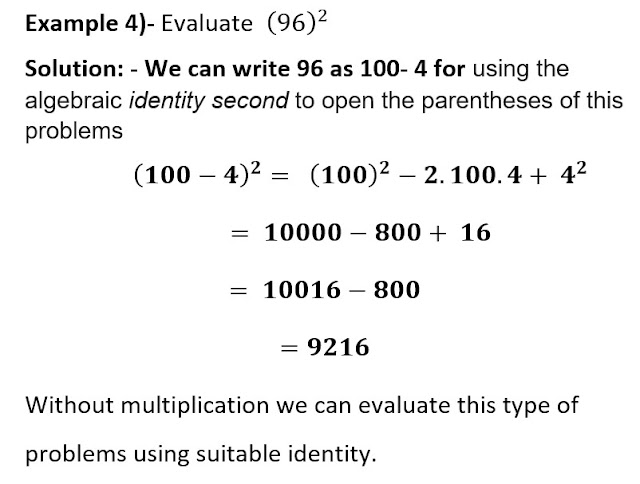
Similarly, we can use the above-mentioned identities to factorize algebraic polynomials and evaluate values like examples 3 and 4.
From the above illustration 8, we can conclude that identity second is obtained by first with substitution of b by (-b). Similar results can be obtained for five and six, seven & eight.
Note:- The number of identities is not fixed they are written only for convenience.